With industrialization and technological advancement, the production process is receiving more and more attention. Every company hopes to have higher production efficiency to reduce costs, improve product quality and meet market demand. The production cycle refers to the process from the purchase of raw materials to the sale of finished products. It includes design, production, packaging and sales. In fact, the length of the production cycle is closely related to production efficiency.
Generally speaking, if the production efficiency is high, the production cycle will be shortened. High productivity means businesses can complete all work processes faster, saving time, manpower and resources. In this way, companies can produce products faster to meet market demand. In addition, the shortened production cycle will also give companies more time to research, develop and innovate, thereby maintaining a competitive advantage.
Today, when it comes to plastic products, thermoformed product and injection molded part are the two most commonly seen forms. Injection molding manufacturers and thermoforming manufacturers also attach great importance to shortening the production cycle of their projects. The time required to complete a cycle of producing parts is a very critical parameter in the production process, so understanding the cycle time of producing parts is the key to improving production efficiency.
In this blog post, we will explore the complexity of the thermoforming production cycle, explore the various factors that affect the thermoforming production cycle, and provide valuable suggestions for thermoforming manufacturers to reduce production and operating costs.

Understand the production cycle
Cyclic manufacturing is the one that starts when the manufacture of a product is dispatched to its suppliers (including the lead time for order placement and other processing time), up to the delivery stage. The industry denotes the complete period of acquiring raw materials, completing the production, through processing, and being stored into the warehouse (translation: the time spent on stages of developing technologies used and storing of the product, that is fabrication cycle) whereas agriculture plantation stand for the entire period of making soil ready for plantation, producing crop, and storage of the product till harvesting.

It consists of production preparation time, process processing time, production time, quality inspection time, transportation and warehousing time, labor process interruption time, etc. There are two situations of labor interruption: One is technical interruption which takes the place in the subsequence conducive to production, like backs of the nature drying and chilling of the labor products or other. The other is organizational interruption which is reliant on the organizational conditions of the production process. Produced by organization of purpose, such as time spent on the way to work, time out waiting for processing, time out waiting for assembly and transportation, etc.

The essence of the requirements put forward by modern production planning and control methods is: the given task is to serve as the conduit for an accurate model of the production process flow and the right intention to manage the four fundamental target parameters of production control (high use ratio, low inventory, short production cycle, and just-in-time). avoid grammar mistakes formed by subject-verb agreement. It is necessary to break down the production cycle into individual parts and start with their examination in the initial stage.
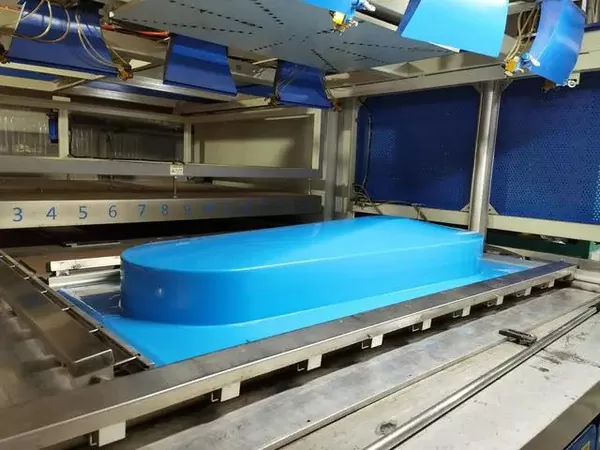

Materials
Selecting the appropriate material to reduce cycle's time is one of the fundamental issues in thermoforming production. There are several factors to consider:There are several factors to consider:
1. Material Type and Thickness
At difference in greenhouse gas emission lies in the different materials selected which result in different production time and outputs. Thermal conductivities of different materials differ a great deal, and this will directly affect the duration of the product heating during thermoforming manufacturing, as well as the cooling period of the product after molding. Due to the use of thick-gauge materials, there are such patterns at the stage of heating: high time resources and more suitable for the production of large or thick large-sized components analysis which increases the cooling time after molding and the difficulty of demolding. Thin gauge sheet would not need a long time for heating and cooling, so the latter process would be faster as well.
2. Board Quality and Consistency
When it comes to thermoforming production, whereby the product produced is imperfect or defective, it causes the smoothness of the entire production process to be significantly interrupted. This is important because otherwise, if the product is found to be defective, the production (process) is likely to be corrected, resulting in a very high volume jobs and this dynamic is counterproductive to our main goal. Regarding raw materials, substandard or non-homogeneous have a heating effect that is not uniform, the product quality tors out the flat sheet can be affected due to the warping during the heating process. High-quality, uniform wall thickness blanks provide a smoother and more fairly accurate prediction heating and forming process, helping to reduce production times and increase thermoforming productivity.

3. Whether the Material has Been Pre-Processed?
If the material for a specific purpose has already been pre-treated, for example if the material has incorporated color or there is any protection against UV or multiple-layer barrier, then its application will be favorable. These types of materials do not go through a regular or simpler heating processes in the heating segment, and therefore the cycle time of the thermoforming production process is required to go up.

Mold Design and Maintenance
The mould used in the thermoforming process is essential to the attainment of the precision part and cycle timing efficiencies. Several aspects of tooling design and care can influence the thermofoming process:Several aspects of tooling design and care can influence the thermofoming process:
1. Mold Complexity
When it comes to employing molds with undercuts and other intricate features, the cycle time is lengthened and thus it is difficult to know whether the material flows all through the mold or not because the mold is complex. To the contrary, typical faster to produce and more simply designed molds ultimately produce shorter molding cycles.

2. Mold Surface Finish
Adopting a high shine or glossy finish of the contact faces of molds reduces the amount of extra heating or cooling time needed to make the process of releasing the parts more easy, thus shortening the cycle time.
3. Mold Condition
After the tool has been worn or damaged out, there are some defects on the parts of the consumer goods such as scratching and missing which leads to increasing cycles to correct or adjust the pieces. Tooling standardization as well as so guard regular maintenance and on-time repair can lead to sustained speeds, as they sequence the manufacturing process.

Machine and Process Control
Equipment of thermoforming and the control system including it, all are such significant factor, which do optimizing cycle time optimization. Key factors to focus on include:Key factors to focus on include:
1. Heater Configuration and Efficiency
The way the heaters and the power they generate impact the way the material reaches forming temperature, and the initial stage of the cycle, is one of the most important hops that make the cycle work. Charitably, well-functioning and good-condition heaters are capable of heating the matter quicker and thus shorten the time needed for the mold closing and starting to shape the specific part.

2. Vacuum and Pressure Systems
The efficacy of a vacuum or pressure systems to inject the hot material in the mold may influence the cycle time. Systems with high power and equally powerful designs will attain uniformity of shape more rapidly and reliably. They will shape the material faster and, thus, save on time.
3. Control System Tuning
Calibrating of process control parameters for specific materials and parts geometries, which leads to a lower wastage time, is essential for optimizing the cycle time. Some of the factors which could lead to more efficient operations when these things are aptly regulated include temperature profiles, vacuum levels and part cooling mechanisms.

Waste Management and Human Value
The work environment and human element in the thermoforming process can often be the X-factor in driving faster or slower cycle times:The work environment and human element in the thermoforming process can often be the X-factor in driving faster or slower cycle times:
1. Workflow and Maintenance Schedules
By providing organising scanning the production lines, reducing fault downtime, and keeping cleanness and maintaining equipments, the shortest possible cycle time can be produced.

2. Operator Skill and Training
Experienced operators with experience in thermoforming process who also know specific requirements for materials and part making can do more informed decisions and thereby reduce cycle time with quicker setup and subsequent processing.
3. Automation and Robotics
Having automation and robotic systems can be a key factor for continuous operations with more precision than human workers could have. Such processes are designed to wrap up tedious, time-consuming tasks, also prone to human error, at a faster pace and higher accuracy rate.

Conclusion
The control of the production process involves many factors, of which only the cycle time is an estimate, and often a guess. Cycle time optimization in thermoforming indeed embodies a multifaceted nature that cannot be dealt with successfully in a mechanical way by considering only materials, tooling, machinery, workforce and the parts involved. Through close appraisal and resolution of these issues, thermoformers will be set to gain efficiency advantages that not only cut costs but also get them to achieve perfect quality of parts and timely performance of their operations. It could be the eliminating the bottlenecks in the control systems, putting an emphasis on the flow of units in the manufacturing environment or doing and investing in research and development – everything that will shorten the cycle time of the thermoforming operation is a step towards a responsive.

Often, firms that want to make the most of the thermoforming process need to review and modify the issues and troubleshoot them critically. This can lead to an improvement in the firm’s productivity and as a result, the profitability. In the fast paced world of manufacturing where there is always lots to do, the skill of reducing cycle time in optimal way is maybe the most crucial one for success.
Estimated cycle time, especially an older model, is crucial, often relying on sell estimated press time (sell press time), existing mold conditions, and flow analysis. John's Plastics Technology columns frequently emphasize the significance of project management in addressing these factors, reaffirming the age-old saying that efficient cycle time management is key to successful thermoforming processes.



