Plastic molding processes include: injection molding, extrusion molding, compression molding, blow molding, calendar molding, rotational molding, vacuum forming (thermoforming), casting (cast molding), slush molding, tape molding, foam molding, transfer molding (injection molding process), winding molding, etc.
In this blog, we’ll detail the differences between thermoforming and compression molding.
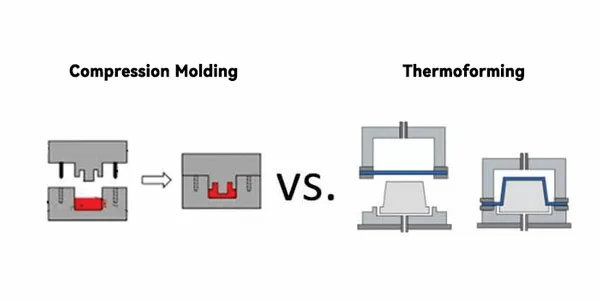
Different Principles
Thermoforming is a process that heats a plastic sheet, uses vacuum suction to adsorb it to the surface of the mold, and heats it while using vacuum suction to make it close to the surface of the mold to achieve the forming effect.
Compression molding is a process in which heat-softened plastic is placed in a hot-pressing mold, shaped under a certain amount of pressure, and then cooled.
Different Manufacturing Processes
Thermoforming
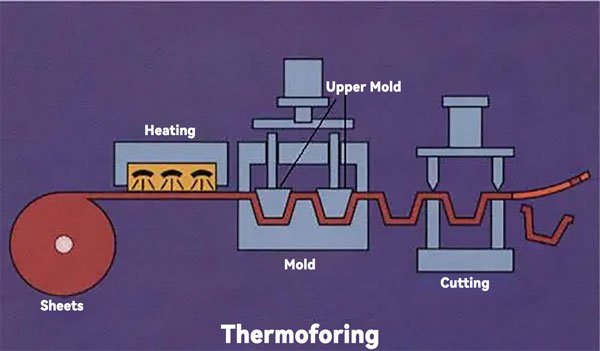
Thermoforming is a plastic processing technology. The main principle is to heat a flat hard plastic sheet to soften it, then use vacuum to adsorb it to the surface of the mold, and then cool it to form.
Vacuum forming process flow:
Plastic sheet - cutting - sheet fixing - heating - forming - demoulding - edge removal - finished product. Thermoforming is formed by vacuum adsorption, while compression molding mainly uses heating and pressure compression molding.
Compression Molding
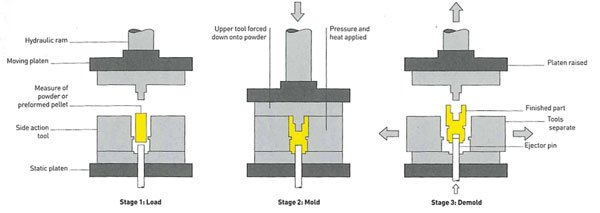
Compression molding is a plastic processing (also rubber processing) method that heats and pressurizes plastic or rubber materials into products in a closed mold cavity.
The compression molding process is divided into feeding, mold closing, exhausting, curing, demoulding and mold cleaning. If the product has inserts that need to be sealed during compression molding, the inserts should be placed before adding molten material. The main controlled process conditions are pressure, mold temperature and compression molding time. In addition, there is a special form of compression molding method, which is to compact the powdered plastic first, then take out the blank from the mold, heat it in a furnace to the melting point, so that the plastic pellets melt into a whole, and after cooling, the product or Semi-finished product.
Compression molding is usually suitable for products that require high-volume production and high precision requirements, such as electronic accessories, auto parts, etc.
Thermoforming is suitable for products that require high surface finish and smooth lines, such as various advertising guides, display casings, etc.
Different Applications
Thermoforming is suitable for products that require high surface finish and smooth lines, such as various advertising guides, display casings, etc. Thermoformed products are mainly used in the electronics and electrical appliance industries, food industry, hardware tools, cosmetics industry, toy industry, daily necessities industry, medicine, health care products, automobiles, stationery, cultural and sports supplies and other industries.

Compression molding is usually suitable for products that require high-volume production and high precision requirements, such as electronic accessories, auto parts, etc.
Compression molding is mainly used for the molding of thermosetting plastic materials (thermosetting resins), such as phenolic, melamine formaldehyde, urea formaldehyde and other plastics. It is also used to manufacture unsaturated polyester and epoxy resin plus glass fiber reinforced plastic products. Thermoplastic materials (thermoplastic resins) are also formed using this method, such as polyvinyl chloride records. However, when thermoplastic plastics are compressed, the mold must be cooled before the product is demoulded, and the mold must be reheated before the next plastic components is formed, so the production efficiency is very low. Compression molding is also a very important molding method in the rubber industry. The rubber material is cut or punched into simple shapes, added to the heated mold, and vulcanized while forming. The product is also demoulded while hot. Many rubber model products such as sealing gaskets and shock-absorbing products (such as rubber rings and rubber sheets) are produced using this method.

Advantages and Disadvantages
Thermoforming
Advantages:
No cracking or deformation: The material of thermoformed panels is stable and not easily deformed or cracked by the environment.
Scratch-resistant, stain-resistant and fade-resistant: Thermoformed panels have good wear resistance and stain resistance, and are not prone to scratches or stains while maintaining bright colors.
Rich colors and realistic wood grains: It can imitate a variety of wood textures and provide rich color choices.
Seamless PVC film pressing molding process: No edge sealing is required, which reduces the risk of glue opening and facilitates daily maintenance.

Disadvantages:
Relatively short service life: Due to the limited service life of the PVC film material on the surface of the thermoformed board, its durability is poor compared to other solid wood or furniture made of other materials.
Not suitable for use in the kitchen: Since thermoformed panels are not resistant to high temperatures, the heat generated when smoking in the kitchen may burn the surface of the panels, so it is not recommended to use thermoformed panel cabinets in the kitchen environment.
Compression Molding
Advantages:
The production efficiency is high and it is easy to realize professional and automated production.
The product has high dimensional accuracy and good repeatability.
The surface is smooth and does not require secondary modification.
It can form products with complex structures at one time.
Because of mass production, the price is relatively low.
Disadvantages:
It requires a lot of molding costs, long processing time, and the workpiece surface is not smooth enough.

Different Materials
There are also differences in composite materials selection between molding and vacuum forming. Molding is suitable for thermoplastics with certain toughness, such as ABS, PC, PVC, etc., and the color, hardness, texture, etc. of these materials can be customized according to needs. Thermoforming is more suitable for thinner plastic sheets, such as PET, PETG, etc. At the same time, the color and texture of these materials need to be selected before production.

The main materials used in thermoforming are thermoplastic sheets such as PVC, PETG, ABS, PC, and PP.
Material requirements for thermoforming:
1. Thermoforming can only produce products with relatively uniform wall thickness (generally the chamfers are slightly thinner), and cannot produce plastic products with widely varying wall thicknesses.
2. The wall thickness of pressure forming is generally within 1 Within the range of 2mm or thinner.
3. The stretch degree of thermoformed products is subject to certain restrictions. The diameter-to-depth ratio of thermoformed plastic containers generally does not exceed 1, and in extreme cases it must not exceed 1.5mm.
4. The dimensional accuracy of pressure forming process is poor, and its relative error is generally more than one percent.

Compression molding mainly uses thermosetting plastics, such as phenolic resin, epoxy resin and glass fiber reinforced plastics.

Different Manufacturing Process
The production process of thermoforming generally includes steps such as mold making, material pretreatment, material adsorption, heating forming and post-processing.
The production process of compression molding generally includes the steps of thermosetting plastic preparation, impregnation, pressing and heat curing.

Different Appearance Effects
There are also differences between molding and thermoforming in terms of appearance. The surface of the molded finished product is usually smooth, with good reflection and tactile feel, while the surface of the thermoformed part has small bumps and is slightly rougher to the touch than the molded part, but it has better waterproofness, transparency and flexibility, while also It can increase certain anti-counterfeiting performance.

Different Molds
Thermoforming Mold
A kind of mold that uses plastic plates and sheets as raw materials to form some relatively simple plastic products (male or female mold). The principle is to use the vacuum opening method or the compressed air molding method to make the plastic plates or sheets fixed on the concave mold or punch mold be heated. When softened, it is deformed and attached to the cavity of the mold to obtain the desired molded product. It is mainly used in the production of some daily necessities, food, and toy packaging products.
Due to the low vacuum pressure during molding, pressure forming molds are mostly made of cast aluminum or non-metallic materials, and the structure is relatively simple.

Compression Molding Mold
Compression molding includes two structural mold types: compression molding and injection molding. They are a type of mold mainly used to shape thermosetting plastics, and their corresponding equipment is a pressure forming machine.
The compression molding method heats the mold to the molding temperature (usually 103°-108°) according to the characteristics of the plastic, then puts the measured compression molding powder into the mold cavity and feeding chamber, closes the mold, and the plastic is heated under the action of high heat and high pressure. It appears as a softened viscous flow, and after a certain period of time, it solidifies and becomes the desired shape.
The compression mold is mainly composed of a cavity, a feeding cavity, a guide mechanism, an ejection component, a heating system, etc. Injection molds are widely used in packaging electrical components. Compression molds are made from basically the same materials as injection molded parts molds.

Conclusion
To summarize, there are some clear differences between compression molding and thermoforming that apply to different production needs. When selecting a molding process, the selection should be based on specific product needs and comprehensively consider all factors to better enhance production efficiency and product quality.





